The Town of Falmouth’s Eco-Toilet Project is looking at the management of nutrient inputs to groundwater as part of an overall wastewater management strategy. The Town of Falmouth has investigated the efficacy of diversion toilets or eco-toilets for the management of nutrient inputs to groundwater with specific reference to nitrogen and phosphorus.
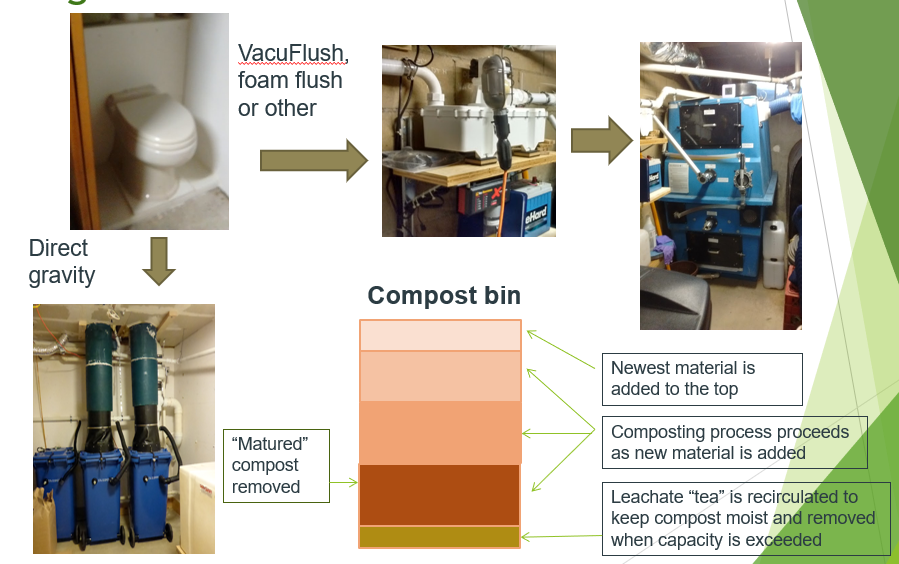
Eco-toilets are appliances that provide for the separation and routing of bodily waste (urine and/or feces and toilet paper) from residential sanitary wastewater, which is additionally comprised of greywater from various sources, such as sinks, showers or laundry wastewater. The investigation of eco-toilets in nitrogen sensitive areas stems from the theory that diverting nitrogen from wastewater reduces overall nitrogen entering groundwater via the septic tank-leach field system and may offer cost savings compared with other wastewater treatment and disposal methods. Two types of eco-toilets are investigated here: composting toilets and urine-diverting toilets.
Ecological sanitation or “eco san” is an age-old sanitation strategy that aims to manage human waste products in ways that sustainably maximize resource value and the health of people and ecosystems. Some example eco san practices include utilizing eco-toilet systems, harvesting rainwater, irrigating with greywater and composting food scraps. All of these practices are based on the foundation of appreciating and valuing resources (like water, nutrients, clean air, healthy soil, etc.) that are essential to the existence of life on earth. Eco san has become a fringe concept in most modern societies around the globe because of the wholesale loss of human connection with nature and the natural cycles of the ecosystems within which we all live and depend upon.